VIDEO
Products
Streaming
Deliver flawless live video to any audience, anywhere
OTT Apps
Launch and monetize your own branded TV and mobile apps
Spark Encoder
Tap into hardware encoding that's compact and powerful
Broadcaster App
Go live straight from your phone or tablet with studio-quality control
Features
BoxCast Flow
Ensures smooth playback even on shaky networks
Sharing
Instantly clip, share, and amplify your broadcasts
Producer
Create professional streams right from your browser
Third-Party Encoders
Use the gear you love with our support of RTMP and SRT
AUDIO
Mixing Station Anywhere
Control your digital mixer in real time from anywhere
Mixing Station Web
Mix, manage, and monitor live audio in a browser from anywhere
Compatible Mixers
Connect your digital mixer to Mixing Station and Mixing Station Web
INDUSTRIES
House of Worship
Reach and engage your congregation wherever they worship
Sports
Stream games with professional quality for fans everywhere
Local Government
Bring transparency and connection to your community broadcasts
Business
Power your corporate events, webinars, and live streams
LEARN
Blog
Insights, trends, and tips for the audio/video community
Tech Tips
Quick how-tos and deep dives on the latest streaming technology
Guides
Essential tips and expert strategies to expand your reach
Newsletter
Stay up to date with product news, best practices, and more
Podcast
Hear stories and strategies from our customers and experts
DISCOVER
Customer Stories
Explore real-world success stories to inspire your organization
Webinars
Get all the details and register for our next live webinar
Events
Join us at an upcoming conference and meet with our team
Broadcasting, Live Streaming Destinations, Live Streaming Software, How To Live Stream

BoxCast Team • December 20, 2022
This post covers the factors that influence your ability to broadcast content in 4K and the recommended bandwidth requirements for 4K live streaming. Wondering what upload speeds you need to stream in 4K? Keep reading, friend.
To live stream video content, you need ample bandwidth. Your required 4K streaming bandwidth depends on the type of compression you use on the video. Use the formula below to see what upload speed you need to stream in 4K.
If you need a refresher about what Mbps means, learn what bitrate is and why it matters for live streaming.
Most software and hardware encoders compress the video using H.264 (aka AVC), but recently more encoders, like the BoxCaster Pro, use H.265 (or HEVC) to compress the video. When using HEVC, you only need half the bandwidth of AVC. If you’re interested in learning more, check out this article that details the differences between H.254 and H.265.
Even with good compression, video content still requires a significant amount of bandwidth. For example, YouTube recommends sending 34 Mbps for 4Kp30, and 50 Mbps for 4Kp60.
In addition to needing high internet speed for 4k streaming, you need to factor in more bandwidth for your audio (typically in the 128–320 Kbps range) and a small amount more for overhead. Then double it — you should plan to always stay at 50% or less of available bandwidth in case of disruptions.
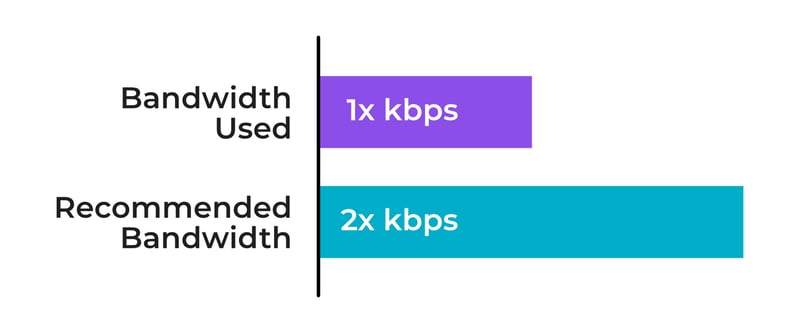
For example, if you stream a 1080p60 broadcast to YouTube, you might use 6,000 Kbps for video, 128 Kbps for audio (YouTube’s recommended audio setting), and 50 Kbps for overhead. Doubling this means you need at least 12,356 Kbps of total available bandwidth.
Factor in all the bandwidth and compression variables from the example we described above using this formula:
6,000 kbps for video +
128 kbps for audio +
50 kbps for overhead =
6,178 kbps x 2 for safety =
12,356 kbps total bandwidth
Calculating your bandwidth should get you to a good place in estimating what you need to live stream. However, don't forget about why you need to transcode...
Don't forget: If your streaming service doesn’t provide cloud transcoding, you’ll need to add those up for every level you wish to provide to viewers.
Transcoding is when you send the streaming provider one high-quality bitrate stream from your encoder, and they take that and create multiple lower bitrate options for your viewers. A live streaming provider like BoxCast does this automatically for you.
It’s very important to stream multiple bitrates to your viewers. That way, if their internet is less than stellar, the player will move them to a lower bitrate automatically instead of buffering. Buffering nearly always results in a loss of viewership.
For example: You can send a stream in 1080p at 6 Mbps, and the streaming provider will pass through that high-quality bitrate, but then offer your viewers bitrates at 4 Mbps, 2 Mbps, and 1 Mbps as well. The player will automatically show the viewer the highest-quality version their internet can handle.
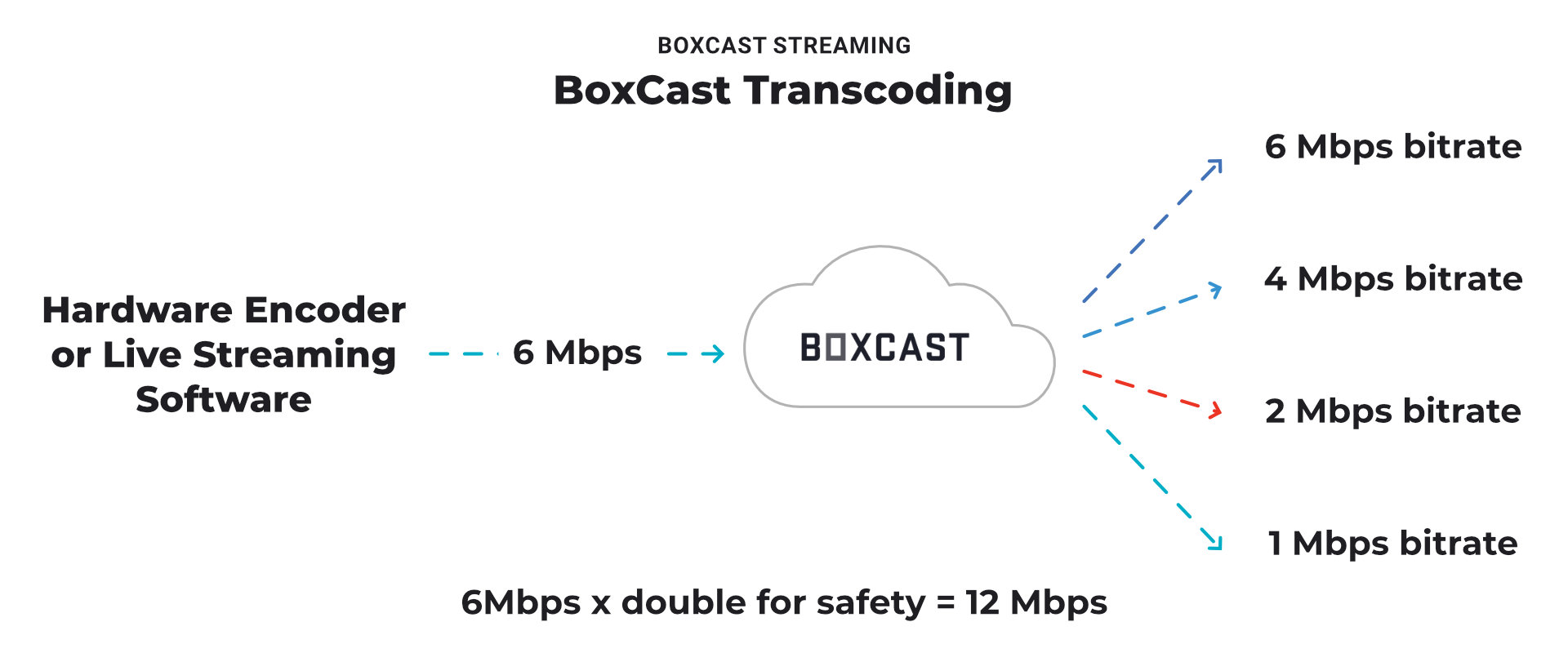
If your streaming provider doesn’t provide cloud transcoding, you’ll need to send all of these bitrates yourself, which means you’ll need much more bandwidth. In the example above, you’d need 6 Mpbs + 4 Mbps + 2 Mbps + 1 Mbps = 13 Mbps x 2 for safety = 26 Mbps ... and that’s just for the video!

BoxCast helps grow your audience with live video. It's that simple:
This means there are two different speeds to think about: upload and download. In case that doesn't make sense, here are some real-life examples of the differences between the two.
Our primary concern for live video streaming is upload speed because we're sending information. You can have the best live streaming hardware available, but if your internet is spotty, your live stream video won’t look good (or it’ll take forever to reach your viewers).
To figure out what your current internet upload speed is, you can visit Speedtest. Check your internet speed and run a free speed test here.
Just remember that running a speed test is only an indicator of your speed during that test — it won’t account for drops in internet speed. So if you run a speed test and everything looks fine, but you’re still having internet issues, you’ll want to reach out to your streaming provider or ISP to find out if the internet is dropping out unexpectedly.
4K streaming seems, at a glance, to be all the rage. Many devices are being sold to consumers claiming 4K compatibility. Your viewers can watch 4K streaming content on most newer smart TVs, gaming consoles, set-top boxes (like Apple TV, Fire TV, and Roku), and computers. That said, while 4K-compatible devices and TVs are becoming increasingly common, 4K content isn’t as standard as you’d think. A lot of 4K streaming content is offered through services like Netflix and HBO Max, which offer videos on demand (VOD) — not live — which means they don’t have to worry about 4K uploading bandwidth.
While it does seem that 4K streaming is here to stay and will be used more in the future, it still uses enough bandwidth (for the broadcaster and the viewer) and enough people still use older devices for 1080p to still be the standard for live streaming now. It’s much more widely used and is generally of high enough quality for live streaming viewers to be more than happy with.
To learn more about BoxCast's advanced video cloud infrastructure, check out how BoxCast encodes, ingests, transcodes, and delivers live video streaming at scale.
In order to stream in 4K quality, you’ll need to send a bitrate of at least 15 Mbps and have a 4K-compatible encoder and streaming service. You’ll also want to make sure your viewers have the ability to view the stream in 4K, and/or offer more than one bitrate (recommended).
The viewer needs a download speed of around 50 Mbps to reliably watch 4K streams. So-called high-speed internet from most ISPs usually only starts at around 25 Mbps.
It’s not recommended to broadcast or send a 4K stream over a Wi-Fi connection, because stability would likely be an issue. If you’re watching a 4K stream and have at least a 30 Mbps connection and a strong router, you can likely view a 4K stream over Wi-Fi. 50 Mbps is recommended.
4K live streaming requires a significant amount of upload speed, and HEVC compression enables broadcasting at half the bandwidth of previous video encoders. However, streaming in 1080p is still more of an industry standard, and is compatible with more viewers and broadcasters’ capabilities. Learn more about broadcasting in ultra HD with these articles:
© 2026 BoxCast. All Rights Reserved. | +1-888-392-2278